|
KPIs KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site where page links may lead to other sites or go HOME
BATTERIES - COST - STANDARDIZATION - HOME - HYDROGEN - LOAD LEVELLING - PAYD - RANGE ANXIETY - RECOVERY - SERVICE STATIONS |
|
KPIs specifically help determine a company's strategic, financial, and operational achievements, especially compared to those of other businesses within the same sector.
KPIs can also be more anecdotal, measuring foot traffic in a store, employee retention, repeat customers, and quality of customer experience, among others.
By setting KPIs a company enables their team to make smart business decisions about the direction of all current projects, so measure a company's success versus a set of targets.
The relative business intelligence value of a set of measurements is greatly improved when the organization understands how various metrics are used and how different types of measures contribute to the picture of how the organization is
performing. KPIs can be categorized into several different types:
- Process or activity measures focus on how the efficiency, quality, or consistency of specific processes used to produce a specific output; they can also measure controls on that process, such as the tools/equipment used or process training
- Outputs are result measures that indicate how much work is done and define what is produced
- Outcomes focus on accomplishments or impacts, and are classified as Intermediate Outcomes, such as customer brand awareness (a direct result of, say, marketing or communications outputs), or
- End Outcomes, such as customer retention or sales (that are driven by the increased brand awareness)
Project measures answer questions about the status of deliverables and milestone progress related to important projects or initiatives.
NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT - INNOVATION
Innovation is recognized as one of the top three business priorities by 84% of executives.
Research & Development (R&D) KPIs are essential for tracking the performance of R&D programs.
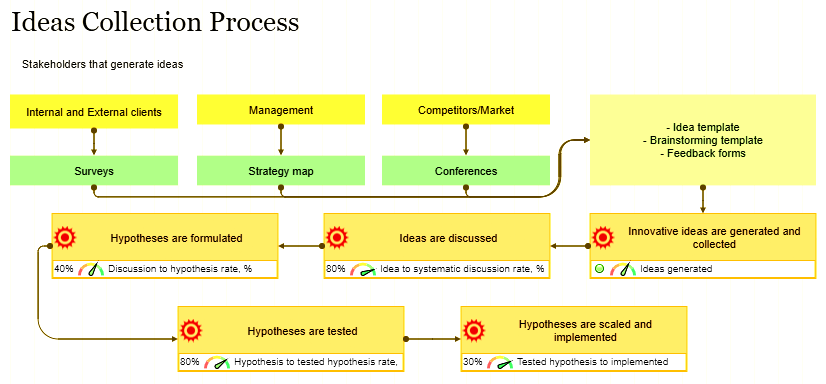
The top 3 KPIs are made of:
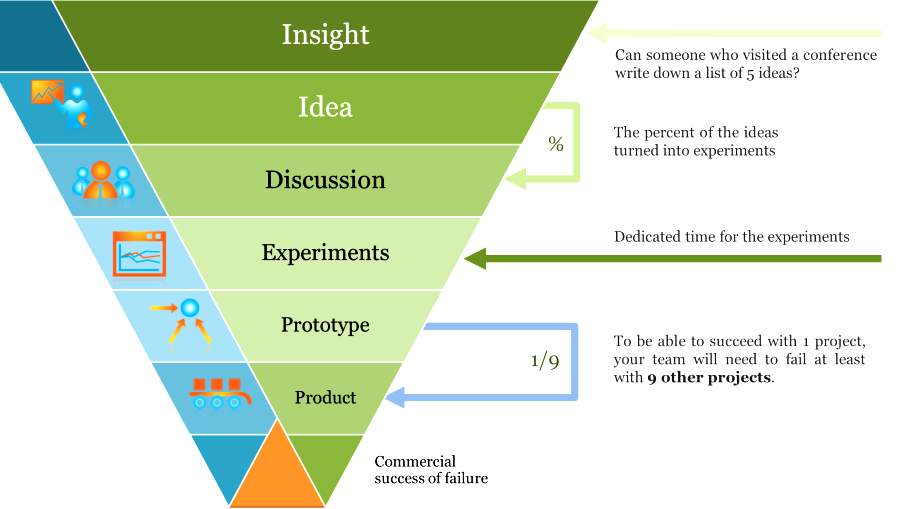
Typical KPIs used for innovation: * The number of innovative initiatives that became successful in a certain amount of time *
Rvenue generated by innovations - The barrier for approving new ideas is too high - Bureaucracy dominates over common sense - Where short-term profits are more important than long-term value for the customers - Where employees are always busy housekeeping and simply don’t have time to think creatively - Where informational silos limit the exchange of information between departments
CLIMATE CHANGE
Scientists have been measuring temperature rise consistently for many years while politicians have been doing their best to ignore them. Even employing spin doctors to generate propaganda to confuse the electorate, playing down our changing climate.
Politicians have allowed themselves to risk the stability of planet earth as they concentrated on wealth creation and empire building. Money and property development are the enemy of
The KPIs relating to global warming are:
4. Forest fires 5. Rising sea levels 6. Flooding
The six end results are directly linked to the millionaires and billionaires who made their fortunes from exploiting the system, without any thought for balancing their abuses.
KPIs relating to stabilization will be exactly the reverse, linked to the measure taken to effect reversal, such as:
- Zero emissions transport - Balancing the economy sustainably - Carbon neutral housing - Renewable energy generation - Decarbonising agriculture - Taxing wealth created without carbon offset
Strategic Measures track progress toward strategic goals, focusing on intended/desired results of the End Outcome or Intermediate Outcome.
When using a balanced scorecard, these strategic measures are used to evaluate progress in achieving the Strategic Objectives depicted in each of the following four balanced scorecard perspectives:
- Customer/Stakeholder - Financial -
Internal Processes
An entire family of measures, including those from each of these categories, can be used to help understand how effectively strategy is being executed.
LINKS & REFERENCE
https://
SMARTNET ™ encapsulates several advanced concepts, such that one might lose sight of the features and advantages of what may be described as a comprehensive transport infrastructure system, to complement policies such as the Automated & Electric Vehicles Act 2018. Please therefore use the header and footer links on associated web pages for ease of subject navigation.
BATTERIES - COST - STANDARDIZATION - HOME - HYDROGEN - LOAD LEVELLING - PAYD - RANGE ANXIETY - RECOVERY - SERVICE STATIONS
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site
|
|
|
This website is provided on a free basis as a public information service. copyright © Climate Change Trust 2021. Solar Studios, BN271RF, United Kingdom. SmartNet™ and SmartGrid™ are trade names belonging to the CCT.
|