|
COP 4 CONFERENCE of the PARTIES DESERTIFICATION 2000
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CHINA 2017 - In 2017 the Conference of the Parties (COP) was held in China. China is one of the biggest users of coal, oil, diesel and petroleum fossil fuels. It is the burning of these fuels that creates greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide, the accumulation of which are causing global warming that is changing our climate to makes deserts of land that was previously arable.
The fourth Conference of the Parties to combat desertification was held in Bonn, Germany from the 11th to 22nd of December 2000.
WHAT IS THE CONVENTION TO COMBAT DESERTIFICATION
The United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification is an agreement to hold meetings to decide how best to help countries experiencing serious drought and/or desertification, particularly in Africa. The UNCCD is a convention to combat soil degradation that makes deserts of previously fertile land that have been farmed out.
The aim of the convention is to mitigate the effects of drought through national action programs that incorporate long-term strategies supported by international cooperation and partnership arrangements. Sadly, climate change is causing a regular loss of land for use in agriculture as global warming accelerates unchecked. That coupled with intensive farming practices that are not sustainable, has created a situation where people have become refugees as victims of developed countries and their use continued use of fossil fuels that create greenhouse gases.
197 PARTIES
The Convention’s 197 parties work together to improve the living conditions for people in drylands, to maintain and restore land and soil productivity, and to mitigate the effects of drought. Though given that climate change is uncontrolled, this is a losing battle at best and very poor compensation to those who the developed world are displacing.
The UNCCD secretariat facilitates cooperation between developed and developing countries, particularly around knowledge and technology transfer for sustainable land management. That is a way of saying they are doing what they can, where they should be dealing with the root cause.
The UNCCD collaborates closely with the other two Rio Conventions; the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), to meet these complex challenges with an integrated approach and the best possible use of natural resources.
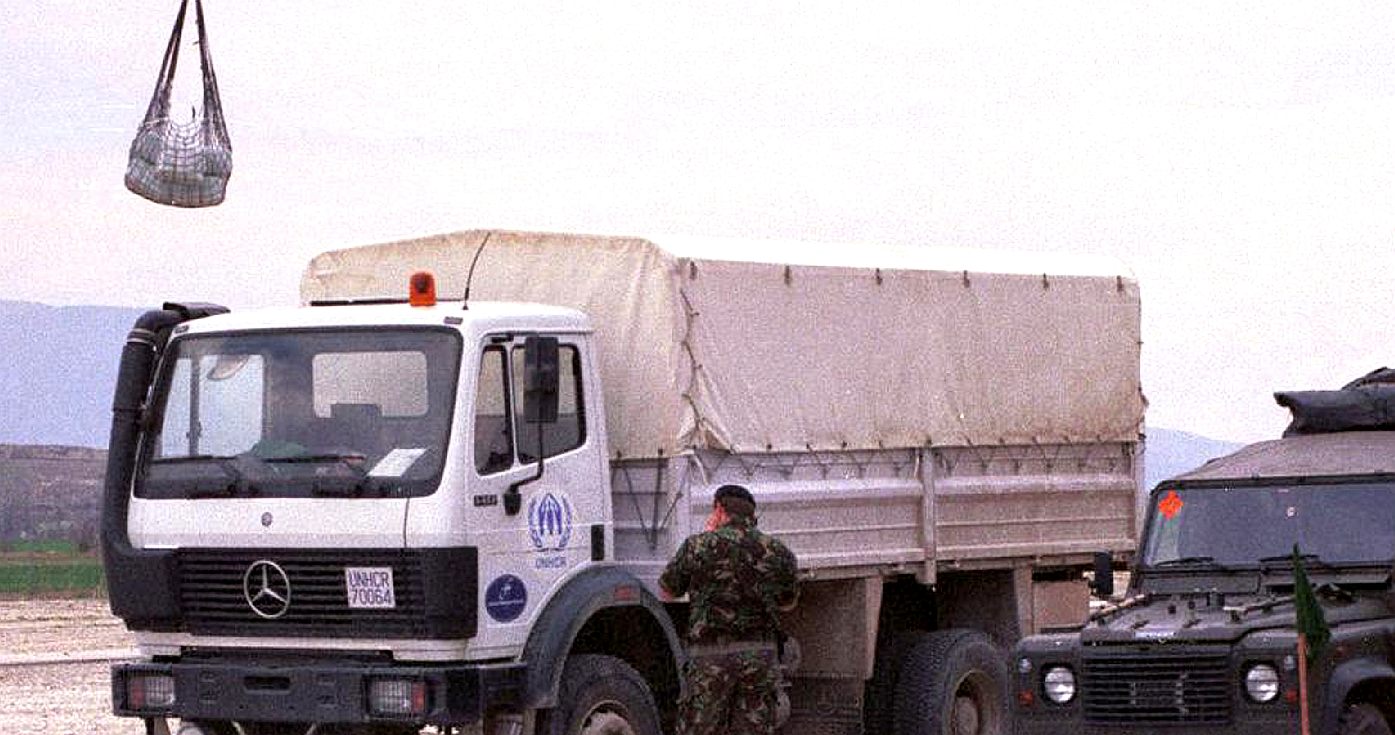
FOOD AID - Desertification gives rise to mass human migration as climate change causes soil degradation, creating refugees who will need feeding as a result of the fossil fuel excesses of the developed world.
THE REGIONS
Five world regions – Africa, Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC), Northern Mediterranean, Central and Eastern Europe - have the important job of deciding how to implement the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD). The Convention Text includes five annexes, which each concern one of these world regions.
The implementation of the UNCCD is organized around these five regional implementation annexes. The annexes specify how the Convention will be implemented for each region and set the focus and content of regional and subregional action programmes. These action programmes provide a framework for regional coordination and collaboration. Though the country Parties of the regions define together how the UNCCD will be implemented, most action takes place at the national level.
DESERTIFICATION COP HISTORY
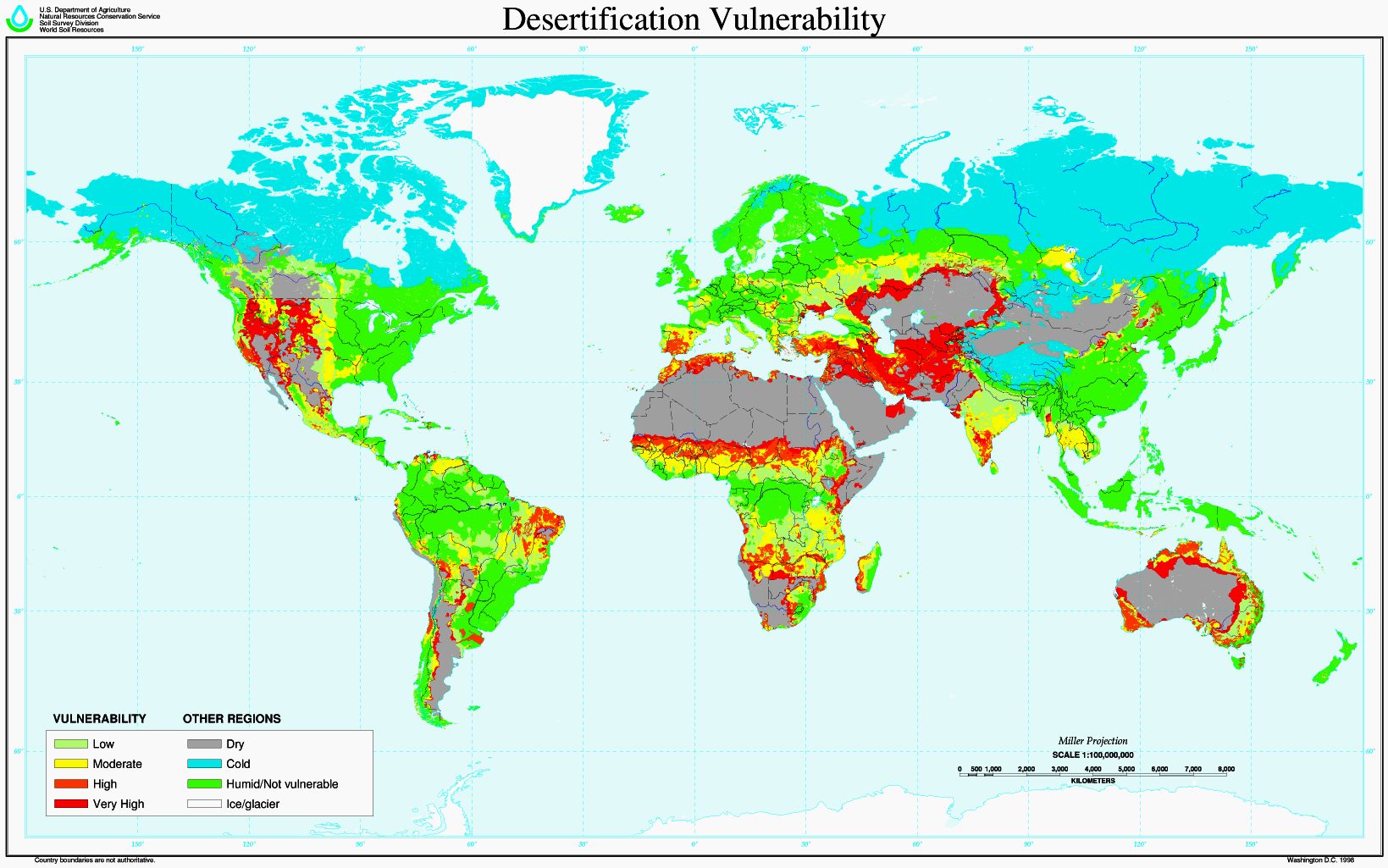
SOIL EROSION - Desertification is a type of land degradation in which a relatively dry area of land becomes a desert, typically losing its bodies of water as well as vegetation and wildlife. It is caused by a variety of factors, such as through climate change (particularly the current global warming) and through the overexploitation of soil through human activity. When deserts appear automatically over the natural course of a planet's life cycle, then it can be called a natural phenomenon; however, when deserts emerge due to the rampant and unchecked depletion of nutrients in soil that are essential for it to remain arable, then a virtual "soil death" can be spoken of, which traces its cause back to human overexploitation. Desertification is a significant global ecological and environmental problem with far reaching consequences on socio-economic and political conditions.
The more land that we lose for to grow crops the greater the food security issue. The more ice that melts from global warming, the more our sea level rises, again, reducing land area. World politics is not working or we would not have these problems. We need to change policies urgently to make politics work for the planet. If that means electing new representatives and executive officers free from conflicts of interest, who understand the urgency of sustainable agriculture, low carbon houses, renewable energy and transport, the electorate should give consideration to voting out the old and voting in new blood for change.
CLIMATE CHANGE COP HISTORY
BIODIVERSITY COP HISTORY
UNCCD CONTACTS
Postal Address
UNITED NATIONS
Switchboard CST contact
Librarian
....
LINKS & REFERENCE
https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld https://www.unccd.int/ https://www.unccd.int/convention/about-convention https://www.un.org/
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This website is provided on a free basis as a public information service. copyright © Climate Change Trust 2019. Solar Studios, BN271RF, United Kingdom.
|