|
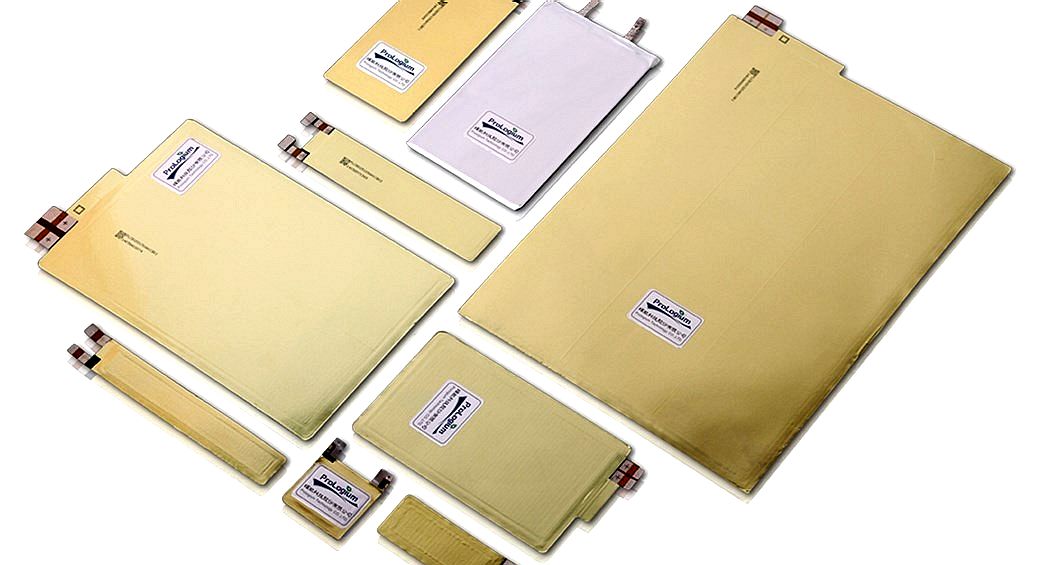
SOLID STATE BATTERIES
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site where page links may lead to other sites, or see HOME
|
|
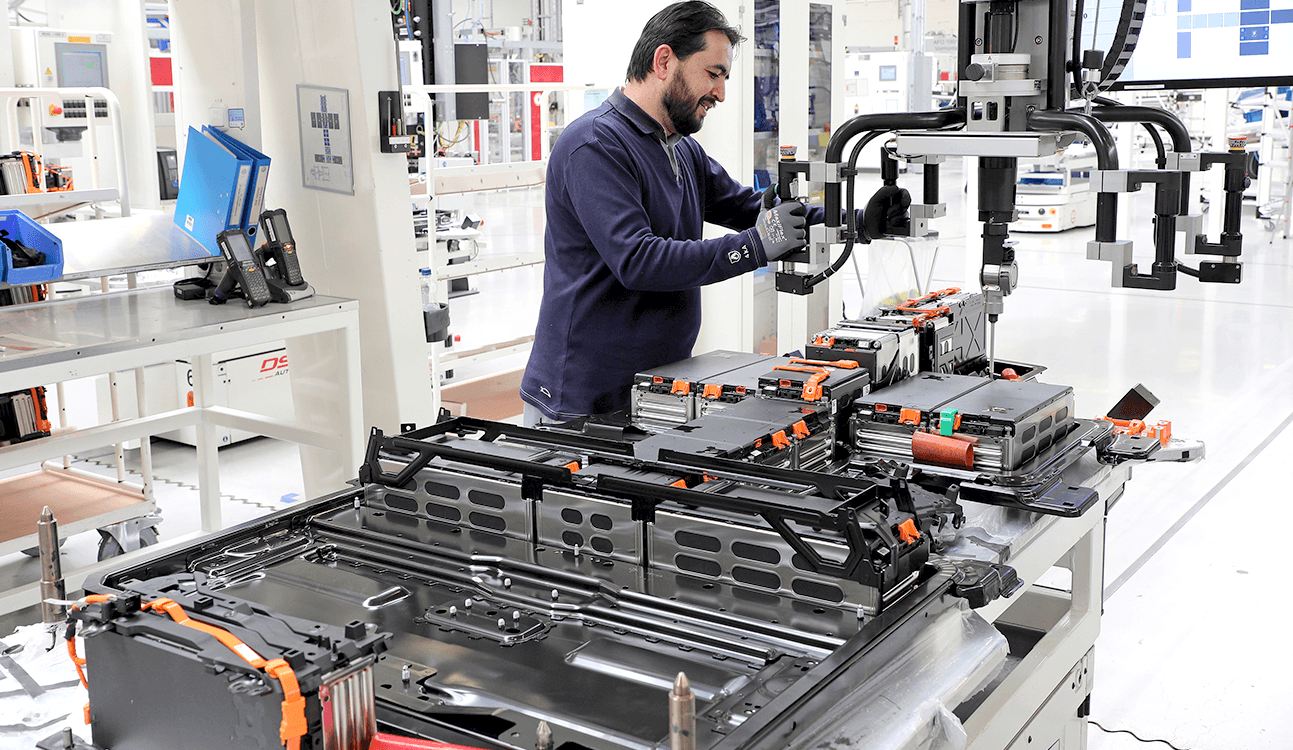
PROGRESS - Until now, solid state batteries have been small. The challenge is to scale them up for electric vehicles and get them into cost effective production. Though the market is advancing at a promising pace, there are still several factors that are profoundly restraining the market growth. Market growth is restricted by high setup and installation cost of solid-state batteries along with complexities in the manufacturing process of the solid-state battery. Solid-state battery manufacturing is a very complex and challenging process. According to the American Chemical Society (ACS), poor conductance of solid electrolyte acts as a major factor that presents complexities during battery manufacturing. Moreover, solid-state batteries are costly as compared to lithium-ion batteries. Thus, manufacturing cost-effective solid-state battery is one of the challenges for the solid-state battery market.
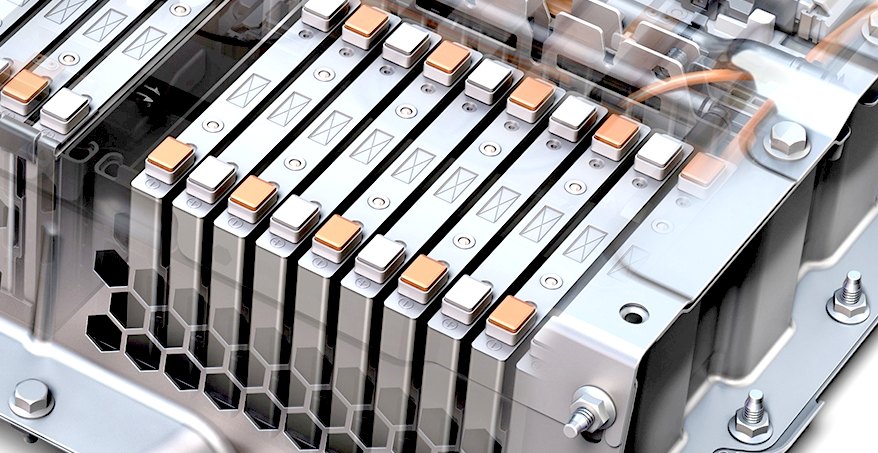
A solid-state battery uses solid electrodes and a solid electrolyte, instead of the liquid or polymer gel electrolytes found in lithium-ion or lithium polymer batteries. Materials proposed for use as solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries include ceramics (e.g. oxides, sulfides, phosphates), and solid polymers.
Challenges to widespread adoption include energy and power density, durability, material costs, sensitivity and stability.
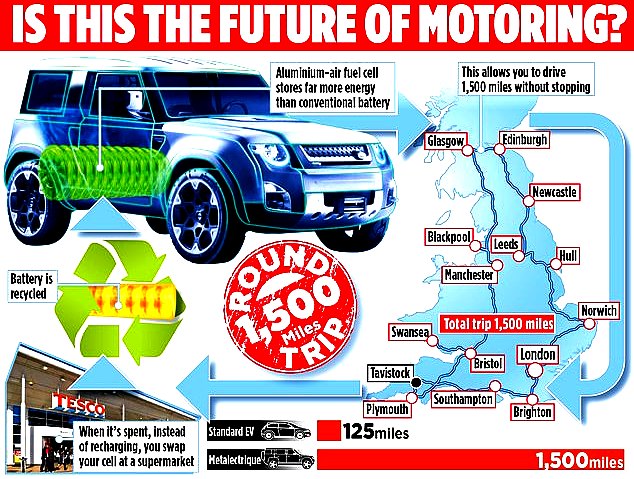
AIR-ALUMINIUM - Another potential high energy density solution is claimed for a safer fuel cell using aluminium and less corrosive electrolyte, by inventor Trevor Jackson.
AUSTIN TEXAS APRIL 2018
Charging a lithium-ion battery too quickly can cause dendrites or “metal whiskers” to form and cross through the liquid electrolytes, causing a short circuit that can lead to explosions and fires. With all-solid-state cells, solid-glass electrolytes are paired with an alkali-metal anode, which cancels out the formation of dendrites.
WET & DRY - The liquid electrolyte in the Leclanché cell on the left is replaced with a moist paste on the dry (drier) battery cell on the right.
SOLID STATE HISTORY
1950s - Several electrochemical systems employed solid electrolytes. They used a silver ion, but had low energy density and cell voltages, and high internal resistance. A new class of solid-state electrolyte, developed by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in the 1990s, was used to make thin film lithium-ion batteries.
2011 - Bolloré launched BlueCar with a 30kWh lithium metal polymer (LMP) battery with a polymeric electrolyte created by dissolving a lithium salt in a co-polymer (polyoxyethylene).
2013 - researchers at University of Colorado Boulder announced the development of a solid-state lithium battery, with a solid composite cathode based upon an iron-sulfur chemistry that promised higher energy capacity.
2014 - researchers at Sakti3 announced a solid-state lithium-ion battery, claiming higher energy density for lower cost. Toyota announced its solid-state battery development efforts and holds the most related patents. In 2015, Sakti3 was acquired by Dyson.
2017 - John Goodenough, the co-inventor of Li-ion batteries, unveiled a solid-state battery, using a glass electrolyte and an alkali-metal anode consisting of lithium, sodium or potassium. Toyota announced the deepening of its decades-long partnership with Panasonic, including a collaboration on solid-state batteries.
Other car makers developing solid-state battery technologies include
BMW,
Honda, Hyundai Motor Company and Nissan. Household appliance maker Dyson
announced and then abandoned a plan to build an electric car. Fisker Inc. claimed that its solid-state battery technology would be ready for "automotive-grade production" in 2023. Spark plug maker NGK is developing ceramic-based solid state batteries.
CAR JANUARY 2020
- Explains solid state batteries, what are they and how
they work?
That’s because most EVs and hybrids rely on electric motors powered by lithium-ion batteries, using the same tech that powers smartphones and laptops. Essentially an evolution on chemical batteries, lithium-ion batteries work well in EVs, but there are better solutions.
The use of a liquid electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries comes with a suite of disadvantages. Capacity and ability to deliver peak charge deteriorates over time and lithium-ion batteries also bleed a lot of heat, requiring weighty cooling systems to be integrated into their design. And thanks to the flammable liquid they contain, lithium-ion batteries can catch fire or even explode if damaged in an accident.
What are solid-state batteries?
Simply put, solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte as opposed to the liquid or polymer gel one found in current lithium-ion batteries, and it can take the form of ceramics, glass, sulphites or solid polymers.
PHYSICS.ORG AUGUST 2018
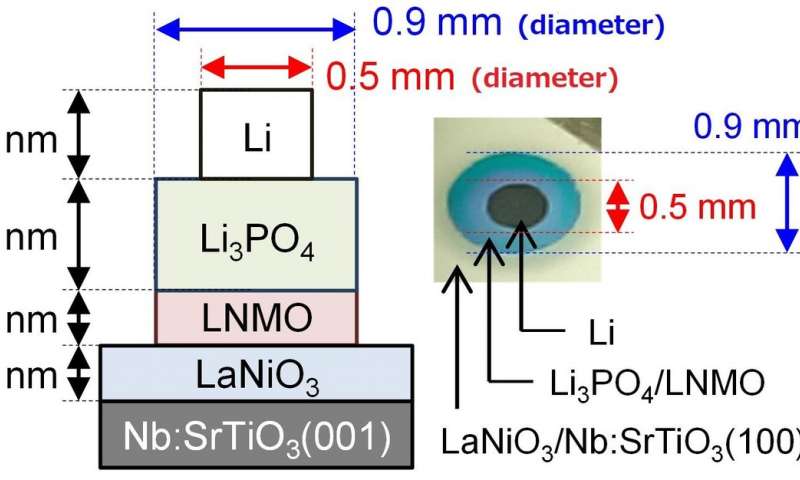
- Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology have addressed one of the major disadvantages of all-solid-state batteries by developing batteries with a low resistance at their electrode/solid electrolyte interface. The fabricated batteries showed excellent electrochemical properties that greatly surpass those of now ubiquitous Li-ion batteries, thereby demonstrating the promise of all-solid-state battery technology and its potential to revolutionize portable electronics.
All-solid-state batteries are a new type of Li-ion battery, and have been shown to be potentially safer and more stable energy storage devices with higher energy densities. However, the use of such batteries is limited due to a major disadvantage—their resistance at the electrode/solid electrolyte interface is too high, hindering fast charging and discharging.
How do solid state batteries work?
Much the same way as a normal battery, if we’re honest. The flow of ions trigger a chemical reaction between the battery’s materials called ‘Redox’ where, when discharging power, oxidation occurs at the anode to create compounds with free electrons, which deliver electric energy, and reduction at the cathode which sees compounds gain electrons and thus store power. When a battery is charged the process is reversed.
Much like lithium-ion batteries, when delivering power in solid-state batteries, aka discharging, positively charged ions travel through the electrolyte from the negative electrode (anode) to the positive one (cathode). This leads to a build up of positive charge in the cathode which attracts electrons from the anode. But as the electrons can’t travel through the electrolyte they have to travel across a circuit and thus deliver power to whatever it’s connected to, say an electric motor.
During charging, the opposite happens with ions flowing to the anode building up a charge that sees electrons pulled to it across a circuit from the cathode. When no more ions will flow to the negative electrode, the battery is considered fully charged.
Solid-state batteries have been around for a while, but are only used for small electronic devices like RFID tags and pacemakers and in their current state are non-rechargeable. As such, work is being done to allow them to power larger devices and be recharged.
What makes solid-state batteries the next big thing?
Drawbacks
Charging ahead
WIRED.CO.UK SEPTEMBER 2017 - What is a solid-state battery? The benefits explained
In 2017, Toyota announced plans to have solid-state batteries in electric cars by 2020, while the Dyson electric car could also use solid-state battery technology developed by Sakti3 – a battery technology firm Dyson acquired in 2015.
What are the benefits of solid-state batteries?
The main benefits are batteries that are smaller, higher-capacity and cheaper than current liquid-based lithium-ion batteries. In 2014, Sakti3 announced it was approaching a point where it could produce a battery with twice the density of current batteries at a fifth of the cost. They’re also non-flammable and, in theory, could last longer and charge faster.
As the Samsung Galaxy Note 7 proved, the cost of getting a battery design wrong can be huge. Current lithium-ion batteries are flammable and they also create a lot of heat, which in electric cars means lots of extra gear to contain and dissipate it. An electric car with a solid-state battery could remove all the cooling elements in favour of a larger battery, and therefore longer range, or reduce the size of the battery while retaining the same range and cutting the cost.
Current batteries are also notorious for having short lifespans. Constant charging and discharging slowly erodes the performance of the battery, which is why a two-year-old iPhone often struggles to get through a whole day of use on one charge.
According to Ilika, a developer of solid-state batteries for Internet of Things devices, they could increase ‘cycle life’ from two years to 10 years. A Wall Street Journal report suggested this could result in greater potential for product recycling after being used in the vehicle, such as in homes or commercial energy storage.
This all sounds great, when can I get one?
Toyota and Dyson both believe solid-state batteries could be in final products by 2020, but there’s no guarantee this will happen. As ever with technology, there’s a huge difference between a technology that works on a small scale and one that’s ready for mass-market production. Watch this space. By Andy Vandervell
BATTERY DEVELOPMENT
Since the early batteries, chemists have been experimenting relentlessly to improve the energy density and life cycle of cells based on silver and iron, nickel and cadmium, nickel-metal-hydride and now lithium based batteries that are the basis of most electric vehicle packs. Zinc and aluminum are less costly metals showing promise as primary and even secondary cells.
POWERING BUSES & TRUCKS - These EV service stations provide load leveling mobility security from renewable solar and wind. This system is the only (and the original) proposal that might refuel electric trucks, buses, SUVs, vans and of course cars.
ELECTRICITY
Electricity is the most convenient way of transmitting clean, alternative energy, from the point of origin (conversion from natural harvesting) to the end user.
Fortunately for humans, electricity is linked to magnetism, a force that can be harnessed to attract or repel, and convert a generated or stored potential difference (such as in batteries) from electrons traveling in a metal conductor, to rotational or linear movement.
This incredible property gives us electric motors and generators. We take it for granted, but it is a miracle of nature. We are living in the age of electricity where heating and lighting is electric, and computers allow us to control just about everything.
The main problem about generated electricity is storing it. This may have been solved in theory by the SMARTNET FASTCHARGE service stations for electric vehicles. The inventor has kept how this system works a secret since 1991, because he was too far ahead of his time. Even now it is risky to start divulging proprietary know-how in patent applications, because patents are expensive, with a limited shelf life of only 20 years, where trademarks may be renewed indefinitely and copyright lasts for 50 years after the death of the author.
FUSION | BIOFUELS | GEOTHERMAL | HYDRO-ELECTRIC | SOLAR | WAVE & TIDAL | WIND
LINKS & REFERENCE
https://phys.org/news/2018-08-limits-li-ion-batterieselectrodes-all-solid-state-batteries.html https://paultan.org/2018/04/03/all-solid-state-battery-cells-developed-by-ut-austin-researchers/ https://www.wired.co.uk/article/what-is-solid-state-battery-toyota-dyson https://www.carmagazine.co.uk/car-news/tech/solid-state-battery-ev/ http://fortune.com/2014/09/18/sakti3-lithium-ion-battery/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid-state_battery https://news.stanford.edu/2015/04/06/aluminum-ion-battery-033115/ https://www.southampton.ac.uk/engineering/research/projects/aluminium_air_battery.page http://aluminiumair.co.uk/ https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-7592485/Father-eight-invents-electric-car-battery-drivers-1-500-miles-without-charging-it.html
ENERGY CRISIS - Some countries act as though there is no energy crisis where they have an abundance of fossil fuel reserves, but they will be unable to milk the remainder of the world with the allure of cheap fossil fuels and energy independence for renewables becomes the norm. We must help those blinded by kleptocratic policies to stop killing species and warming the planet.
Please use our A-Z INDEX to navigate this site
|
|
|
This website is provided on a free basis as a public information service. copyright © Climate Change Trust 2021. Solar Studios, BN271RF, United Kingdom.
|